



Nächste Seite: 7.5 Deklarationen und Headerfiles,
Aufwärts: 7. Funktionen
Vorherige Seite: 7.3 Rückgabewerte von Funktionen
Inhalt
Index
7.4 Felder als Parameter
Statische Felder können analog zu ihrer Deklaration als Funktionsparameter
übergeben werden. Allerdings müssen alle Dimensionen, außer der
höchsten Dimension, zum Compilierungszeitpunkt bekannt sein.
Wir betrachten als erstes Beispiel die Ausgabe eines
(statischen oder dynamischen) 1D-Feldes,
d.h., Vektors
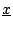 der Länge n.
(siehe Ex740.cc)
der Länge n.
(siehe Ex740.cc)
Struktogramm:

#include <iostream.h>
//------------------------------------------------------------
// Print elements of a vector (length n)
//
void PrintVec(const int n, const double x[])
{
int i;
cout << endl;
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
cout << " " << x[i];
}
cout << endl << endl;
return;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------
main()
{
const int N=4;
int n,i;
double f[N] = {1,2,3,4};
double *df;
cin >> n;
df = new double [n]; // Allocate dynamic array
// Initialize df
...
PrintVec(N,f); // Print static array
PrintVec(n,df); // Print dynamic array
}
|
Als nächstes betrachten wir die Ausgabe eines statischen 2D-Feldes,
d.h., einer Matrix mit MCOL Spalten und NROW Zeilen.
Hier muß die Anzahl der Spalten als globale Konstante definiert
werden, da ansonsten die nachfolgende Funktion nicht compiliert werden kann.
#include <iostream.h>
const int MCOL=3; // global constant
//------------------------------------------------------------
// Print elements of a matrix
// (nrow rows and fixed number MCOL of columns)
//
// doesn't compile
//void PrintMat_fix(const int nrow, const double a[][])
// doesn't help to fix that
//void PrintMat_fix(const int nrow, const int ncol,
// const double a[][])
//
void PrintMat_fix(const int nrow, const double a[][MCOL])
{
int i,j;
cout << endl;
for (i=0; i<nrow; i++)
{
cout << "row " << i << ":";
for (j=0; j<MCOL; j++)
{
cout << " " << a[i][j];
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl << endl;
return;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------
main()
{
const int NROW=4; // local constant
double a[NROW][MCOL] = { ... };
PrintMat_fix(NROW,a); // print static matrix
}
|
Leider können wir die Funktion PrintMat_fix nur für
statische 2D-Felder (Matrizen) anwenden, und dann auch nur für
solche mit NCOL=3 Spalten - schon eine Matrix
double aa[7][9] kann mit dieser Funktion nicht mehr ausgegeben
werden.
Jedoch können wir das 2D-Feld als 1D-Feld der Länge NROW*MCOL
auffassen und so die Funktion dahingehend verallgemeinern, daß
beliebige statische 2D-Felder und als 2D-Felder interpretierbare
dynamische 1D-Felder
(wie in Version 2 auf Seite ![[*]](crossref.png) )
übergeben werden können.
(siehe Ex740.cc)
)
übergeben werden können.
(siehe Ex740.cc)
#include <iostream.h>
//------------------------------------------------------------
// Print elements of a matrix
// (nrow rows and ncol columns)
//
void PrintMat(const int nrow, const int ncol, const double a[])
{
int i,j;
cout << endl;
for (i=0; i<nrow; i++)
{
cout << "Row " << i << ":";
for (j=0; j<ncol; j++)
{
cout << " " << a[i*ncol+j] ;
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl << endl;
return;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------
main()
{
const int NROW=7, MCOL=9; // local constants
double a[NROW][MCOL] = { ... }; // static matrix a
double *b; // dynamic matrix b
int nrow,ncol;
cin >> nrow; cin >> ncol; // read dimensions of b
b = new double [NROW*MCOL]; // allocate b
// initialize matrix b
...
// output matrices
PrintMat(NROW,MCOL,a[0]); // Pointer on first row
PrintMat(nrow,ncol,b);
}
|
Da die Funktion PrintMat
ein 1D-Feld erwartet (also ein Zeiger),
muß vom statischen 2D-Feld a ein Zeiger auf die erste
Zeile der Matrix übergeben werden.
Daher erscheint a[0] in der entsprechenden Rufzeile.




Nächste Seite: 7.5 Deklarationen und Headerfiles,
Aufwärts: 7. Funktionen
Vorherige Seite: 7.3 Rückgabewerte von Funktionen
Inhalt
Index
Gundolf Haase
2004-01-15
![]() der Länge n.
(siehe Ex740.cc)
der Länge n.
(siehe Ex740.cc)

![[*]](crossref.png) )
übergeben werden können.
(siehe Ex740.cc)
)
übergeben werden können.
(siehe Ex740.cc)