istream und ostream gearbeitet werden.
(siehe FileIO_b.cc)
// FileIO_b.cc
#include <iostream.h>
#include <fstream.h>
int main()
{
int n, tf;
bool bf;
// variables for IO streams
istream *myin;
ostream *myout;
// input file
istream* infile = new ifstream("in.txt");
// output file
ostream* outfile = new ofstream("out.txt");
// Still standard IO
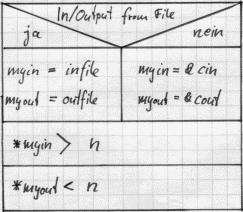
// Decide whether terminal-IO or file-IO should be used
cout << "Input from terminal/file - Press 0/1 : ";
cin >> tf;
bf = (tf==1);
if (bf)
{ // Remaining IO via file
myin = infile;
myout = outfile;
}
else
{ // Remaining IO via terminal
myin = &cin;
myout = &cout;
}
(*myout) << "Input: ";
(*myin) >> n;
// check
(*myout) << endl;
(*myout) << "Input was " << n << endl;
(*myout) << endl;
(*myout) << "This is an additional output" << endl;
delete outfile; // don't forget it
delete infile;
return 0;
}
|
Eine sehr komfortable Möglichkeit des Umschaltens der Ein-/Ausgabe mittels Kommandozeilenparameter ist in den Beispielen zu finden. (siehe FileIO_c.cc) (siehe FileIO_d.cc)